Junsong Fan

I am currently an Assistant Professor at the Centre for Artificial Intelligence and Robotics, Hong Kong Institute of Science & Innovation, Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAIR, HKISI_CAS). Before that, I received my B.E. degree from the School of Automation Science and Electrical Engineering at Beihang University in 2016, and received my Ph.D. degree at the Center of Research on Intelligent Perception and Computing, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, under the supervision of Prof. Tieniu Tan and Prof. Zhaoxiang Zhang. My research interests include computer vision and machine learning. Specifically, I am curious about open problems in scene understanding, self-supervised concept discovery, and multi-modal perception in open worlds.
selected publications
-
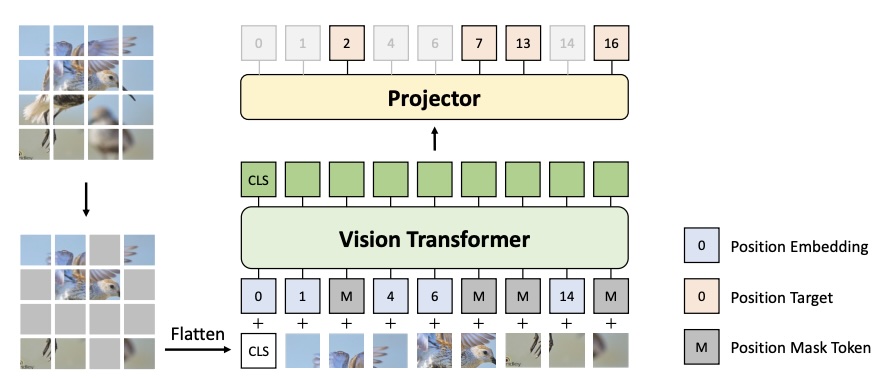 DropPos: Pre-Training Vision Transformers by Reconstructing Dropped PositionsHaochen Wang, Junsong Fan, Yuxi Wang, and 3 more authorsNeurIPS, 2023
DropPos: Pre-Training Vision Transformers by Reconstructing Dropped PositionsHaochen Wang, Junsong Fan, Yuxi Wang, and 3 more authorsNeurIPS, 2023As it is empirically observed that Vision Transformers (ViTs) are quite insensitive to the order of input tokens, the need for an appropriate self-supervised pretext task that enhances the location awareness of ViTs is becoming evident. To address this, we present DropPos, a novel pretext task designed to reconstruct Dropped Positions. The formulation of DropPos is simple: we first drop a large random subset of positional embeddings and then the model classifies the actual position for each non-overlapping patch among all possible positions solely based on their visual appearance. To avoid trivial solutions, we increase the difficulty of this task by keeping only a subset of patches visible. Additionally, considering there may be different patches with similar visual appearances, we propose position smoothing and attentive reconstruction strategies to relax this classification problem, since it is not necessary to reconstruct their exact positions in these cases. Empirical evaluations of DropPos show strong capabilities. DropPos outperforms supervised pre-training and achieves competitive results compared with state-of-the-art self-supervised alternatives on a wide range of downstream benchmarks. This suggests that explicitly encouraging spatial reasoning abilities, as DropPos does, indeed contributes to the improved location awareness of ViTs. The code is publicly available at https://github.com/Haochen-Wang409/DropPos.
@article{wang2023droppos, title = {DropPos: Pre-Training Vision Transformers by Reconstructing Dropped Positions}, author = {Wang, Haochen and Fan, Junsong and Wang, Yuxi and Song, Kaiyou and Wang, Tong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, journal = {NeurIPS}, year = {2023}, } -
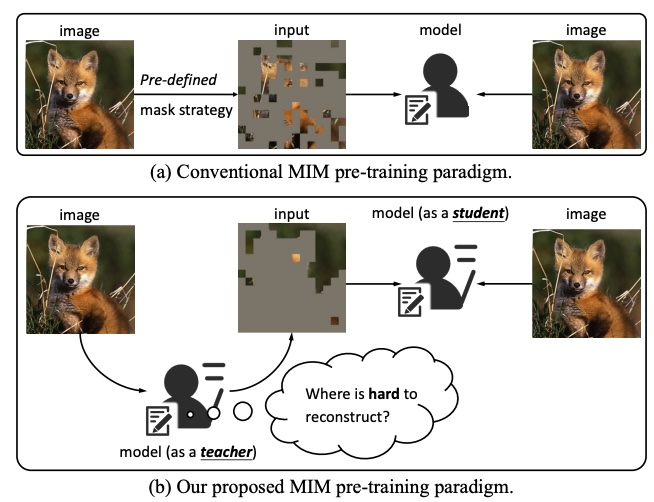 Hard Patches Mining for Masked Image ModelingHaochen Wang, Kaiyou Song, Junsong Fan, and 3 more authorsIn CVPR, 2023
Hard Patches Mining for Masked Image ModelingHaochen Wang, Kaiyou Song, Junsong Fan, and 3 more authorsIn CVPR, 2023Masked image modeling (MIM) has attracted much research attention due to its promising potential for learning scalable visual representations. In typical approaches, models usually focus on predicting specific contents of masked patches, and their performances are highly related to pre-defined mask strategies. Intuitively, this procedure can be considered as training a student (the model) on solving given problems (predict masked patches). However, we argue that the model should not only focus on solving given problems, but also stand in the shoes of a teacher to produce a more challenging problem by itself. To this end, we propose Hard Patches Mining (HPM), a brand-new framework for MIM pre-training. We observe that the reconstruction loss can naturally be the metric of the difficulty of the pre-training task. Therefore, we introduce an auxiliary loss predictor, predicting patch-wise losses first and deciding where to mask next. It adopts a relative relationship learning strategy to prevent overfitting to exact reconstruction loss values. Experiments under various settings demonstrate the effectiveness of HPM in constructing masked images. Furthermore, we empirically find that solely introducing the loss prediction objective leads to powerful representations, verifying the efficacy of the ability to be aware of where is hard to reconstruct.
@inproceedings{wang2023hard, title = {Hard Patches Mining for Masked Image Modeling}, author = {Wang, Haochen and Song, Kaiyou and Fan, Junsong and Wang, Yuxi and Xie, Jin and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {10375--10385}, year = {2023}, } -
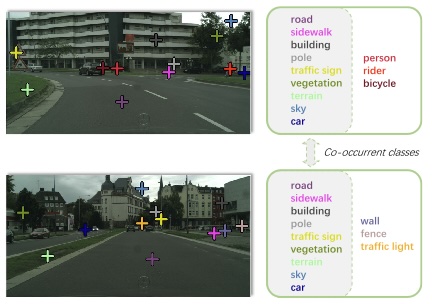 Toward Practical Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation via Point-Level SupervisionJunsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIJCV, 2023
Toward Practical Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation via Point-Level SupervisionJunsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIJCV, 2023Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) aims to reduce the cost of collecting dense pixel-level annotations for segmentation models by adopting weak labels to train. Although WSSS methods have achieved great success, recent approaches mainly concern the image-level label-based WSSS, which is limited to object-centric datasets instead of more challenging practical datasets that contain many co-occurrent classes. In comparison, point-level labels could provide some spatial information to address the class co-occurrent confusion problem. Meanwhile, it only requires an additional click when recognizing the targets, which is of negligible annotation overhead. Thus, we choose to study utilizing point labels for the general-purpose WSSS. The main difficulty of utilizing point-level labels is bridging the gap between the sparse point-level labels and the dense pixel-level predictions. To alleviate this problem, we propose a superpixel augmented pseudo-mask generation strategy and a class-aware contrastive learning approach, which manages to recover reliable dense constraints and apply them both to the segmentation models’ final prediction and the intermediate features. Diagnostic experiments on the challenging Pascal VOC, Cityscapes, and the ADE20k datasets demonstrate that our approach can efficiently and effectively compensate for the sparse point-level labels and achieve cutting-edge performance on the point-based segmentation problems.
@article{fan2023toward, title = {Toward Practical Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation via Point-Level Supervision}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, journal = {IJCV}, volume = {131}, number = {12}, pages = {3252--3271}, year = {2023}, publisher = {Springer}, } -
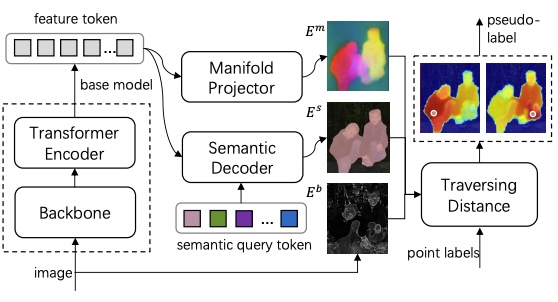 Pointly-Supervised Panoptic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, and Tieniu TanIn ECCV, 2022
Pointly-Supervised Panoptic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, and Tieniu TanIn ECCV, 2022In this paper, we propose a new approach to applying point-level annotations for weakly-supervised panoptic segmentation. Instead of the dense pixel-level labels used by fully supervised methods, point-level labels only provide a single point for each target as supervision, significantly reducing the annotation burden. We formulate the problem in an end-to-end framework by simultaneously generating panoptic pseudo-masks from point-level labels and learning from them. To tackle the core challenge, i.e., panoptic pseudo-mask generation, we propose a principled approach to parsing pixels by minimizing pixel-to-point traversing costs, which model semantic similarity, low-level texture cues, and high-level manifold knowledge to discriminate panoptic targets. We conduct experiments on the Pascal VOC and the MS COCO datasets to demonstrate the approach’s effectiveness and show state-of-the-art performance in the weakly-supervised panoptic segmentation problem. Codes are available at https://github.com/BraveGroup/PSPS.git.
@inproceedings{fan2022pointly, title = {Pointly-Supervised Panoptic Segmentation}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang and Tan, Tieniu}, booktitle = {ECCV}, pages = {319--336}, year = {2022}, organization = {Springer}, } -
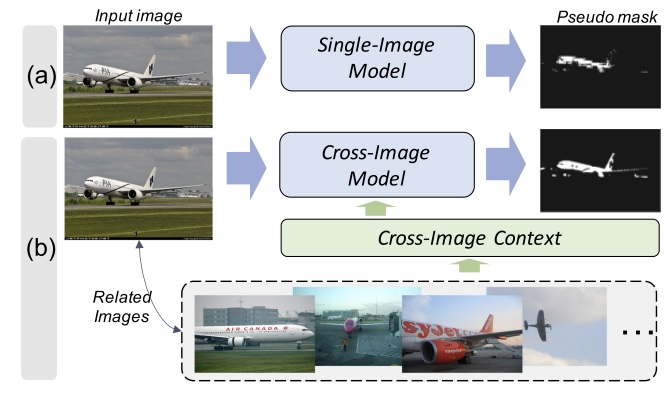 Memory-Based Cross-Image Contexts for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIEEE T-PAMI, 2022
Memory-Based Cross-Image Contexts for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIEEE T-PAMI, 2022Weakly supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) trains segmentation models by only weak labels, aiming to save the burden of expensive pixel-level annotations. This paper tackles the WSSS problem of utilizing image-level labels as the weak supervision. Previous approaches address this problem by focusing on generating better pseudo-masks from weak labels to train the segmentation model. However, they generally only consider every single image and overlook the potential cross-image contexts. We emphasize that the cross-image contexts among a group of images can provide complementary information for each other to obtain better pseudo-masks. To effectively employ cross-image contexts, we develop an end-to-end cross-image context module containing a memory bank mechanism and a transformer-based cross-image attention module. The former extracts cross-image contexts online from the feature encodings of input images and stores them as the memory. The latter mines useful information from the memorized contexts to provide the original queries with additional information for better pseudo-mask generation. We conduct detailed experiments on the Pascal VOC 2012 and the COCO dataset to demonstrate the advantage of utilizing cross-image contexts. Besides, state-of-the-art performance is also achieved. Codes are available at https://github.com/js-fan/MCIC.git.
@article{fan2022memory, title = {Memory-Based Cross-Image Contexts for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, journal = {IEEE T-PAMI}, volume = {45}, number = {5}, pages = {6006--6020}, year = {2022}, publisher = {IEEE}, } -
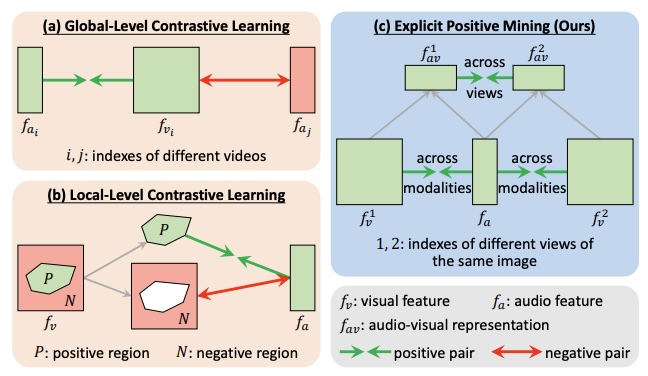 Self-Supervised Predictive Learning: A Negative-Free Method for Sound Source Localization in Visual ScenesZengjie Song, Yuxi Wang, Junsong Fan, and 2 more authorsIn CVPR, 2022
Self-Supervised Predictive Learning: A Negative-Free Method for Sound Source Localization in Visual ScenesZengjie Song, Yuxi Wang, Junsong Fan, and 2 more authorsIn CVPR, 2022Sound source localization in visual scenes aims to localize objects emitting the sound in a given image. Recent works showing impressive localization performance typically rely on the contrastive learning framework. However, the random sampling of negatives, as commonly adopted in these methods, can result in misalignment between audio and visual features and thus inducing ambiguity in localization. In this paper, instead of following previous literature, we propose Self-Supervised Predictive Learning (SSPL), a negative-free method for sound localization via explicit positive mining. Specifically, we first devise a three-stream network to elegantly associate sound source with two augmented views of one corresponding video frame, leading to semantically coherent similarities between audio and visual features. Second, we introduce a novel predictive coding module for audio-visual feature alignment. Such a module assists SSPL to focus on target objects in a progressive manner and effectively lowers the positive-pair learning difficulty. Experiments show surprising results that SSPL outperforms the state-of-the-art approach on two standard sound localization benchmarks. In particular, SSPL achieves significant improvements of 8.6% cIoU and 3.4% AUC on SoundNet-Flickr compared to the previous best. Code is available at: https://github. com/zjsong/SSPL.
@inproceedings{song2022self, title = {Self-Supervised Predictive Learning: A Negative-Free Method for Sound Source Localization in Visual Scenes}, author = {Song, Zengjie and Wang, Yuxi and Fan, Junsong and Tan, Tieniu and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {3222--3231}, year = {2022}, } -
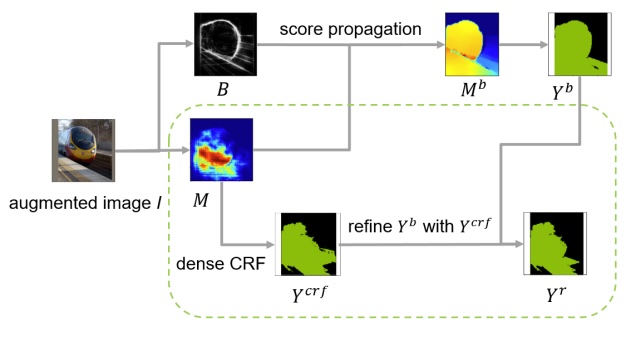 Towards Noiseless Object Contours for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJing Li, Junsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIn CVPR, 2022
Towards Noiseless Object Contours for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJing Li, Junsong Fan, and Zhaoxiang ZhangIn CVPR, 2022Image-level label based weakly supervised semantic segmentation has attracted much attention since image labels are very easy to obtain. Existing methods usually generate pseudo labels from class activation map (CAM) and then train a segmentation model. CAM usually highlights partial objects and produce incomplete pseudo labels. Some methods explore object contour by training a contour model with CAM seed label supervision and then propagate CAM score from discriminative regions to non-discriminative regions with contour guidance. The propagation process suffers from the noisy intra-object contours, and inadequate propagation results produce incomplete pseudo labels. This is because the coarse CAM seed label lacks sufficient precise semantic information to suppress contour noise. In this paper, we train a SANCE model which utilizes an auxiliary segmentation module to supplement high-level semantic information for contour training by backbone feature sharing and online label supervision. The auxiliary segmentation module also provides more accurate localization map than CAM for pseudo label generation. We evaluate our approach on Pascal VOC 2012 and MS COCO 2014 benchmarks and achieve state-of-the-art performance, demonstrating the effectiveness of our method.
@inproceedings{li2022towards, title = {Towards Noiseless Object Contours for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Li, Jing and Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {16856--16865}, year = {2022}, } -
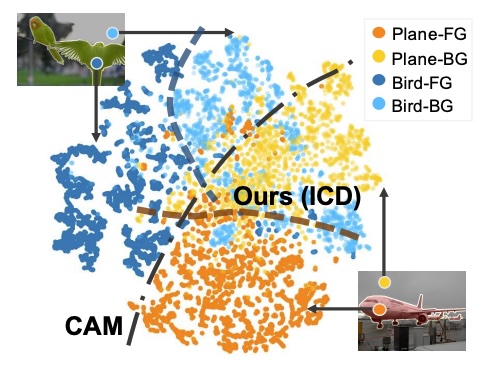 Learning Integral Objects with Intra-Class Discriminator for Weakly-Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Chunfeng Song, and 1 more authorIn CVPR, 2020
Learning Integral Objects with Intra-Class Discriminator for Weakly-Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Chunfeng Song, and 1 more authorIn CVPR, 2020Image-level weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) aims at learning semantic segmentation by adopting only image class labels. Existing approaches generally rely on class activation maps (CAM) to generate pseudo-masks and then train segmentation models. The main difficulty is that the CAM estimate only covers partial foreground objects. In this paper, we argue that the critical factor preventing to obtain the full object mask is the classification boundary mismatch problem in applying the CAM to WSSS. Because the CAM is optimized by the classification task, it focuses on the discrimination across different image-level classes. However, the WSSS requires to distinguish pixels sharing the same image-level class to separate them into the foreground and the background. To alleviate this contradiction, we propose an efficient end-to-end Intra-Class Discriminator (ICD) framework, which learns intra-class boundaries to help separate the foreground and the background within each image-level class. Without bells and whistles, our approach achieves the state-of-the-art performance of image label based WSSS, with mIoU 68.0% on the VOC 2012 semantic segmentation benchmark, demonstrating the effectiveness of the proposed approach.
@inproceedings{fan2020learning, title = {Learning Integral Objects with Intra-Class Discriminator for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang and Song, Chunfeng and Tan, Tieniu}, booktitle = {CVPR}, pages = {4283--4292}, year = {2020}, } -
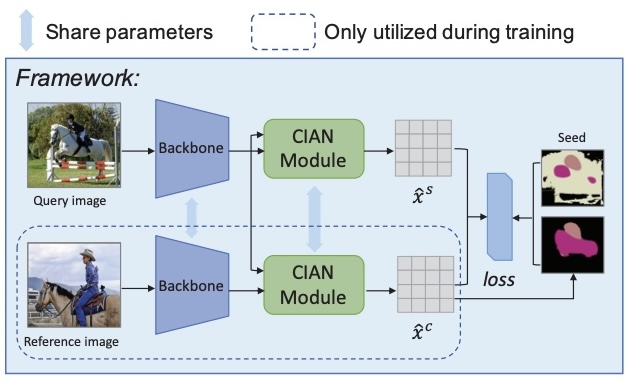 CIAN: Cross-Image Affinity Net for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Tieniu Tan, and 2 more authorsIn AAAI, 2020
CIAN: Cross-Image Affinity Net for Weakly Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, Tieniu Tan, and 2 more authorsIn AAAI, 2020Weakly supervised semantic segmentation with only image-level labels saves large human effort to annotate pixel-level labels. Cutting-edge approaches rely on various innovative constraints and heuristic rules to generate the masks for every single image. Although great progress has been achieved by these methods, they treat each image independently and do not take account of the relationships across different images. In this paper, however, we argue that the cross-image relationship is vital for weakly supervised segmentation. Because it connects related regions across images, where supplementary representations can be propagated to obtain more consistent and integral regions. To leverage this information, we propose an end-to-end cross-image affinity module, which exploits pixel-level cross-image relationships with only image-level labels. By means of this, our approach achieves 64.3% and 65.3% mIoU on Pascal VOC 2012 validation and test set respectively, which is a new state-of-the-art result by only using image-level labels for weakly supervised semantic segmentation, demonstrating the superiority of our approach.
@inproceedings{fan2020cian, title = {CIAN: Cross-Image Affinity Net for Weakly Supervised Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang and Tan, Tieniu and Song, Chunfeng and Xiao, Jun}, booktitle = {AAAI}, volume = {34}, number = {07}, pages = {10762--10769}, year = {2020}, } -
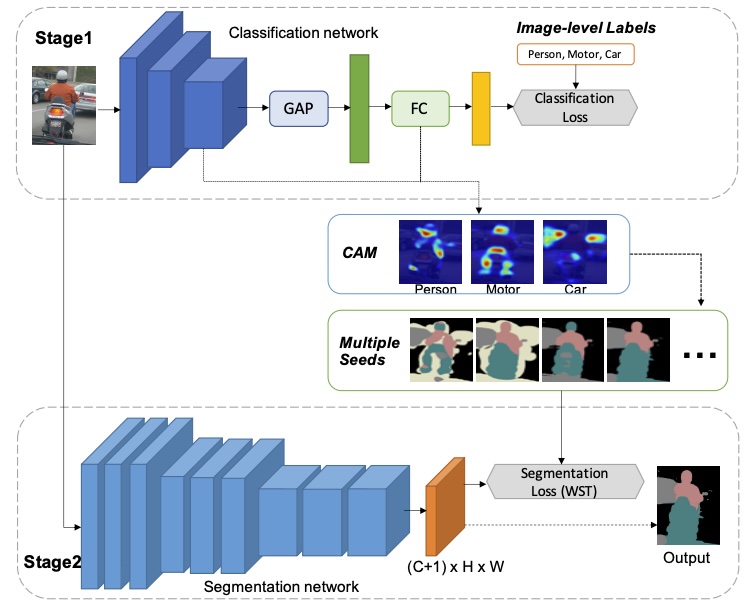 Employing Multi-Estimations for Weakly-Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, and Tieniu TanIn ECCV, 2020
Employing Multi-Estimations for Weakly-Supervised Semantic SegmentationJunsong Fan, Zhaoxiang Zhang, and Tieniu TanIn ECCV, 2020Image-level label based weakly-supervised semantic segmentation (WSSS) aims to adopt image-level labels to train semantic segmentation models, saving vast human labors for costly pixel-level annotations. A typical pipeline for this problem is first to adopt class activation maps (CAM) with image-level labels to generate pseudo-masks (a.k.a. seeds) and then use them for training segmentation models. The main difficulty is that seeds are usually sparse and incomplete. Related works typically try to alleviate this problem by adopting many bells and whistles to enhance the seeds. Instead of struggling to refine a single seed, we propose a novel approach to alleviate the inaccurate seed problem by leveraging the segmentation model’s robustness to learn from multiple seeds. We managed to generate many different seeds for each image, which are different estimates of the underlying ground truth. The segmentation model simultaneously exploits these seeds to learn and automatically decides the confidence of each seed. Extensive experiments on Pascal VOC 2012 demonstrate the advantage of this multi-seeds strategy over previous state-of-the-art.
@inproceedings{fan2020employing, title = {Employing Multi-Estimations for Weakly-Supervised Semantic Segmentation}, author = {Fan, Junsong and Zhang, Zhaoxiang and Tan, Tieniu}, booktitle = {ECCV}, pages = {332--348}, year = {2020}, organization = {Springer}, }